Your car relies on many parts working together for optimal performance. Engine oil is crucial in this system by reducing friction between moving parts and regulating engine temperature. There are many types and grades of engine oil, which can make selecting the right one confusing.
Have you ever felt confused by the codes on motor oil containers? SAE 5W-30, 10W-40 – what do these numbers and letters mean?
Understanding these markings is essential for choosing the best oil for your car’s engine, ensuring smooth operation and a longer life.
Table of Contents
What do the numbers on motor oil mean?
The numbers on a motor oil bottle, like “5W-30,” tell us about its viscosity. Viscosity means how thick the oil is. This thickness is very important because it helps protect the engine.
What Are Engine Oil Grades?
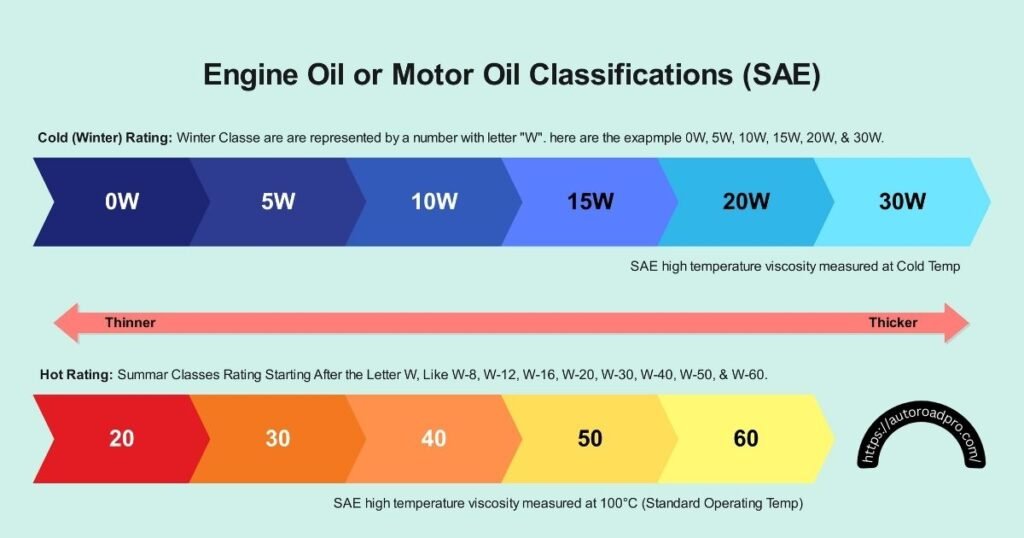
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed a system to categorize engine oils by their viscosity. Viscosity is how thick a liquid is, or how much it resists flowing. Engine oil gets thicker or thinner with temperature changes.
What Does Viscosity Mean for Your Car Motor Oil?
Oil’s viscosity affects how it performs in different temperatures. Each oil grade shows how well the oil works across a range of temperatures. The lower the number, the thinner the oil, and the more easily it flows.
Imagine oil like syrup. If it’s thick, it flows slowly, just like syrup does. Viscosity tells us how hard it is for a fluid to flow.
For an engine, oil must be thin enough to move freely when you start your car, which helps reduce wear on the engine parts.
But when the engine heats up, the oil needs to be thick enough to keep a smooth, protective layer between those moving parts.
Winter Viscosity Explained
The part of the oil grade with a “W” stands for winter. This number tells you how the oil flows in cold temperatures, like when you start your car on a chilly morning.
For example, 0W-30 oil flows better in the cold than 10W-30 oil.
High-Temperature Viscosity
The number after the “W” shows the oil’s thickness at about 100°C or 212°F, which are normal engine operating temperatures.
Higher numbers mean thicker oil, which is good for scorching weather or high-performance cars.
What are the different viscosity grades (e.g., 0W-20, 5W-30, 10W-40)?
Viscosity grades have a “W” which stands for “winter.” The number before the “W” shows how well the oil flows when it’s cold.
For instance, 0W means the oil moves very well in the cold, making it easier to start your car. The number after the “W” tells you how thick the oil is at the engine’s normal operating temperature.
Higher numbers like 30 or 40 mean the oil is thicker, which is good for hot weather or powerful engines.
Why Does Viscosity Matter?
Oil viscosity plays a critical role in engine health.
Thinner oil, with lower numbers, is ideal for cold climates. It flows more easily, which minimizes wear and tear during cold starts. Additionally, thin oils offer better fuel efficiency due to reduced friction within the engine.
Thicker oil, with higher numbers, is better suited for hotter climates and high-mileage engines. It provides a more robust layer of protection between engine components, reducing friction at high operating temperatures.
However, using oil that’s too thick for your climate or engine can be detrimental. Thick oil struggles to flow freely at cold starts, increasing wear and tear.
Conversely, thin oil might not adequately protect hot engines or those with significant wear.
When to Choose 5W-30 vs. 10W-40 Oil?
Deciding whether to use 5W-30 or 10W-40 motor oil in your car depends on where you live and what your car needs. Let’s explore these two options!
5W-30 oil is a great choice if you live in a place with moderate weather. It helps your car start easily in cold weather and provides good protection when the engine heats up.
If you’re in a warmer place or your car has a lot of miles on it, 10W-40 might be better. It creates a thicker layer of oil in the engine, which is great for older engines that have more wear and tear.
It’s important to check your car’s owner’s manual too. It tells you the best oil to use for your specific car to keep it running smoothly.
Why Some Cars Require High-Performance Oil?
High-performance engines work harder and get hotter than regular engines. They need special oils made just for them.
These oils have special stuff mixed in to handle tough conditions. They are often thicker (like 10W-60) to protect the engine better.
What is Single-Grade vs. Multi-Grade Oils?
Motor oils have changed a lot over time. In the past, we used something called single-grade oils, such as SAE 30.
This type of oil kept the same thickness no matter the temperature but wasn’t very flexible for different weather conditions.
Then came multi-grade oils, like 5W-30. These oils are pretty smart because they work like thin oil in cold weather and thick oil in hot weather. That means they’re good to use all year round!
How do viscosity grades affect engine performance?
Choosing the right viscosity grade is crucial. If the oil is too thick when you start your engine, it can cause too much friction and wear out the engine parts.
But if the oil is too thin when the engine is running hot, it might not protect the engine well enough, which could lead to damage.
What are the Motor Oil Classifications?
Motor oil isn’t all the same. Each type has special perks. Let’s explore what makes each one unique!
Conventional oil is the most basic kind. It’s made from crude oil and is the most affordable. This oil works well for many cars and is a solid choice for everyday driving. However, you might need to change it more often.
Synthetic oil is a step up. It’s made from specially engineered molecules. This oil is great for extreme temperatures and lasts longer between changes. But it does cost more.
Synthetic blend oil is the middle ground. It mixes conventional and synthetic oils. This blend boosts performance more than just conventional oil and is cheaper than full synthetic.
What is API Certification for Motor Oil?
The American Petroleum Institute, or API, decides what quality motor oils should have. When you’re checking out motor oil, always look for the API certification donut symbol on the bottle.
The letters after “API,” like SN or SP, tell you about the oil’s performance level. Newer codes mean the oil works better with the latest engines.
How does API certification ensure oil quality?
API certification means the oil meets certain standards for protecting against wear, reducing friction, and controlling deposits. This gives you peace of mind knowing your oil is up to the task.
Other Important Oil Specifications
You might see other acronyms on oil labels, too. ILSAC stands for the International Lubricating Standards and Approval Committee.
They set extra performance standards for gasoline engines, often working alongside the API. ACEA, or the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association, sets oil standards specifically for European cars.
Sometimes, car manufacturers have their oil approval ratings, which ensure the oil is compatible with your specific vehicle.
What Do API and ACEA Ratings on Motor Oil Mean?
Motor oil labels can tell you a lot about the oil’s suitability for your car. API, short for American Petroleum Institute, classifies motor oils into two main categories.
Oils with a service code starting with “S” are for gasoline engines. Those with a code starting with “C” are for diesel engines.
The second letter in the API service code tells you about the oil’s performance level. A higher letter means better protection for newer engines. For instance, API SN is commonly used for modern gasoline engines.
ACEA stands for the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association. This rating is similar to API but focuses on the requirements of European car manufacturers.
Knowing these ratings helps you pick the right oil for your car’s engine, ensuring it runs smoothly and lasts longer.
How do these specifications impact oil performance and compatibility?
Choosing the best motor oil involves considering several important factors. Look at the climate where you live. If it gets really cold, an oil with a lower “W” number helps your car start better in the winter.
Think about how you drive. If you’re often in stop-and-go traffic or like fast driving, your engine works harder. A full synthetic or synthetic blend oil might be best for these conditions.
Also, think about your car’s engine. Newer engines usually need thinner oils like 0W-20 or 5W-30 to run smoothly and use less fuel.
It’s a good idea to check your owner’s manual to find out the right type of oil for your car.
These tips help make sure the oil you choose is just right for your car’s engine and the way you drive. Always double-check with your owner’s manual to make sure the oil fits the car manufacturer’s requirements.
What Happens if I Use the Wrong Motor Oil?
Using the Wrong Oil Grade Can Lead To Several Issues.
Oil that’s too thin won’t protect your engine well enough. This can cause parts to rub against each other and wear out faster.
On the other hand, if the oil is too thick, it can create too much friction. This makes your engine work harder than it should.
Also, using oil with the wrong thickness can lower your gas mileage. This happens because the incorrect oil viscosity can make your engine less efficient.
Lastly, if the oil in your engine is too thick, especially in cold weather, it can be tough to start your car. The oil doesn’t flow as freely, making it harder to crank the engine.
How to Select the Perfect Motor Oil for Your Car?
Your car’s owner’s manual is the best guide for selecting the right motor oil. It includes recommendations tailored to your car’s model, engine type, and the climate you live in.
If you have an older vehicle, it’s a good idea to talk to your mechanic about its specific oil needs.
Climate plays a big role in deciding on motor oil. In colder areas, lighter oils like 5W-30 help your car start better. In warmer places, thicker oils like 10W-40 are better suited.
If your car has been on the road for a long time, a thicker oil can help protect its aging engine. This is especially true if you often take short trips in cold weather, as thinner oils improve cold-start performance.
What are the Signs You Need an Oil Change?
Is your car’s oil dipstick showing black or dirty oil? This means the oil is breaking down and gathering dirt, which is not good for your engine.
Many newer cars have a system that tells you when it’s time for an oil change. Remember, this light is helpful, but it’s best to check your owner’s manual to know exactly when to change your oil.
Has your car been feeling a bit sluggish or making strange noises? These could be signs that your oil is worn out and needs changing.
Conclusion
Knowing what the numbers and acronyms on motor oil labels mean can help you choose the best oil for your car. This choice can keep your engine running smoothly for a long time.
Using the right oil is like investing in your car’s future. It helps your car perform better and last longer!


